Battling Blepharitis: Keeping Your Eyelids Healthy
6 . May . 2025
Author: Clarity Healthcare
Category: Eye Health
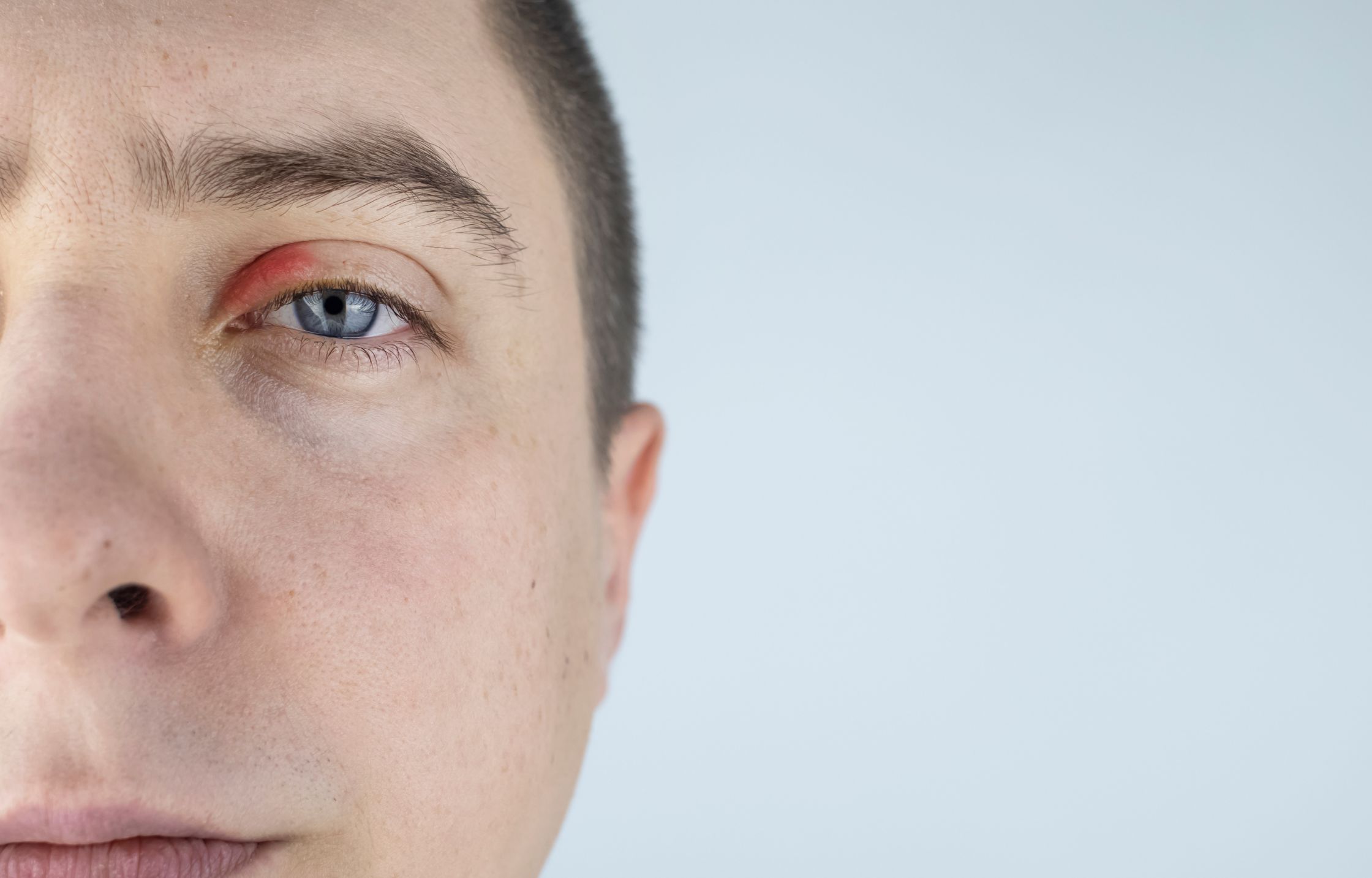
Blepharitis, an inflammation of the eyelids, is a common eye condition that can cause discomfort and irritation. While it’s often not serious, it can be persistent and bothersome. Understanding its symptoms, treatment options, and preventative measures can help you manage this condition and maintain healthy eyelids.
What is Blepharitis?
Blepharitis typically affects the edges of the eyelids, where the eyelashes grow. It can be categorized into two main types:
- Anterior Blepharitis: Affects the outside edge of the eyelid, where the eyelashes are attached.
- Posterior Blepharitis: Affects the inner edge of the eyelid, where the meibomian glands (oil-producing glands) are located.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Blepharitis can manifest in various ways, including:
- Redness and swelling of the eyelids
- Itching or burning sensation
- Watery eyes
- Dry eyes
- Gritty or sandy feeling
- Crusting or scaling of the eyelids, especially in the morning
- Sticky eyelids
- Loss of eyelashes
- Light sensitivity
- Blurred vision
Causes of Blepharitis
Several factors can contribute to blepharitis, including:
- Seborrheic dermatitis: A skin condition that causes flaky, oily skin.
- Bacterial infection: Staphylococcus bacteria are often involved.
- Meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD): Problems with the oil-producing glands in the eyelids.
- Rosacea: A skin condition that causes redness and visible blood vessels.
- Dry eye syndrome: Can contribute to or worsen blepharitis.
- Allergies: Can trigger inflammation of the eyelids.
- Eyelash mites (Demodex): Tiny mites that live in eyelash follicles.
Treatment of Blepharitis
Treatment for blepharitis focuses on managing symptoms and improving eyelid hygiene. Common approaches include:
- Warm compresses: Applying warm compresses to the eyelids for 5-10 minutes several times a day can help loosen crusts and soften oil secretions.
- Eyelid scrubs: Gently cleaning the eyelids with a mild cleanser or eyelid wipes can remove debris and bacteria.
- Antibiotic ointments or drops: Your doctor may prescribe antibiotic medications to treat bacterial infections.
- Steroid eye drops: In some cases, steroid eye drops may be used to reduce inflammation.
- Artificial tears: Lubricating eye drops can help alleviate dry eye symptoms.
- Treating underlying conditions: Addressing conditions like seborrheic dermatitis, rosacea, or dry eye syndrome can help manage blepharitis.
Preventing Blepharitis
While blepharitis can be recurring, you can take steps to minimize flare-ups:
- Maintain good eyelid hygiene: Regularly clean your eyelids with warm compresses and eyelid scrubs.
- Avoid rubbing your eyes: Rubbing can irritate the eyelids and spread bacteria.
- Practice good hand hygiene: Wash your hands frequently, especially before touching your eyes.
- Remove eye makeup before bed: Avoid sleeping with eye makeup on.
- Replace eye makeup regularly: Old makeup can harbour bacteria.
- Manage underlying conditions: If you have seborrheic dermatitis, rosacea, or dry eye syndrome, follow your doctor’s recommendations for managing these conditions.
- Use artificial tears as needed: Lubricating eye drops can help prevent dry eye symptoms.
If you are experiencing persistent blepharitis symptoms, it’s essential to consult with an eye care professional. They can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan for your individual needs.